By Isabeau Ottolini, Environmental Social Scientist
Several months ago, we informed you of the initiative led by Italy, Austria and Greece to register transhumance on the UNESCO list of Intangible Cultural Heritage. Today we have good news!
 During the UNESCO December meeting in Bogota, Colombia, the millennia-old tradition of transhumance was accepted as UNESCO intangible cultural heritage. The day of the decision was quite appropriate since the decision was adopted on December the 11th, the International Mountain Day, as transhumance often takes place in mountain areas. Italy, Austria, and Greece started the UNESCO nomination in 2017; Euromontana congratulates its member organisations involved in this initiative aiming at safeguarding mountains’ specificities.
During the UNESCO December meeting in Bogota, Colombia, the millennia-old tradition of transhumance was accepted as UNESCO intangible cultural heritage. The day of the decision was quite appropriate since the decision was adopted on December the 11th, the International Mountain Day, as transhumance often takes place in mountain areas. Italy, Austria, and Greece started the UNESCO nomination in 2017; Euromontana congratulates its member organisations involved in this initiative aiming at safeguarding mountains’ specificities.
Transhumance is the seasonal movements of livestock and shepherds over ancient routes to the best grazing grounds. It is an economic activity based on a unique relationship between nature and humankind. Moreover, it is one of the most sustainable livestock farming practices thanks to the in-depth knowledge of transhumance herders about the environment, ecological balance, and their animals.
Recognising transhumance as UNESCO heritage is a great victory for Italy, Austria and Greece because it officially acknowledges its uniqueness, as well as its cultural and environmental importance. Also, it can further encourage actions to protect transhumance, as nowadays fewer and fewer people are choosing this way of life. Thereby not only a sustainable economic activity disappears, but also social rituals, food products, handicrafts, to name some examples.
Dario Franceschini, Italian Minister for Cultural Heritage, Activities and Tourism, declared he was “proud of the inscription of transhumance on the UNESCO list of the intangible heritage of humanity. A culture whose origins are lost over time, from which comes a message of integration, not only between landscapes but also between civilizations“.
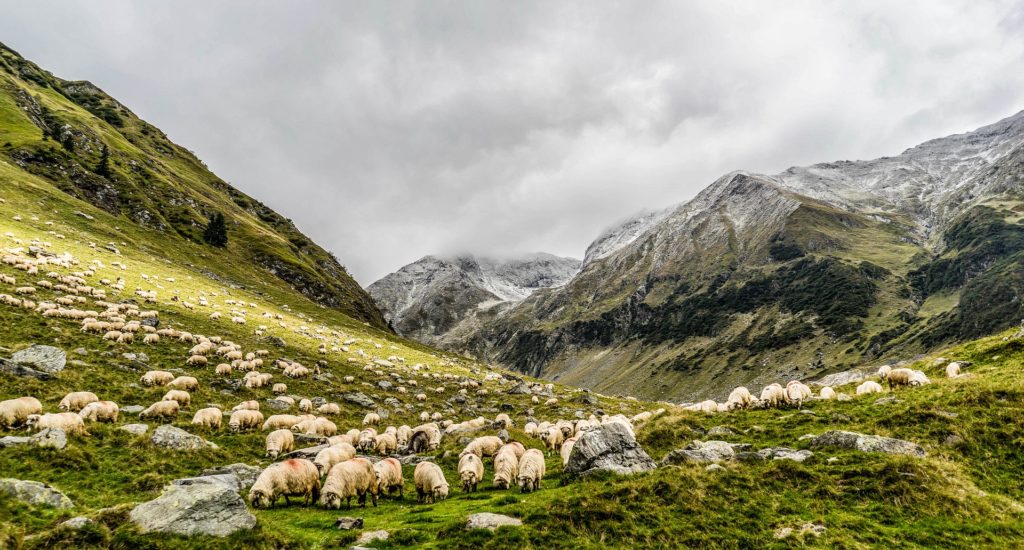

However, many other European countries have similar traditions, often in mountain areas. For instance, in Romania there is the “După coada oilor” and in Norway the “Seterkultur”. And while not all countries joined the nomination, efforts are done to recognise transhumance across Europe’s mountains, like the White paper on transhumance in Spain, or the Wallachian cultural trail in Poland and Slovenia. Moreover, other countries may join the UNESCO protection but first need to succeed in recognising transhumance as cultural heritage at national level. France is for instance currently working on collecting data about its different massifs and the Ministry of Culture is expected to submit the national application in Spring 2020. Likewise, Spain might also join the Italian, Greek and Austrian dossier in February 2021. Scandinavian counties could join later during a second wave of aggregation but first need to get the practice recognised by their respective governments.
Following the good news from the UNESCO session on December the 11th 2019, more efforts can thus be made to aggregate more countries under this protection and better promote the social, cultural and agri-environmental benefits of transhumance. What is your region doing to value and protect transhumance practices?
7 January 2020