In the North West part of Spain, in the region of Galicia, common forest lands are owned and managed by the people living in nearby hamlets. Special laws make sure that all the profit they yield is reinvested in the community. In order to get better benefits the inhabitants of Vincios got involved in an innovative way of exploring the multiple functions of their forests.
Context
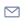
The common forest land of Vincios is located near the city of Vigo, in the region of Galicia, in the North West of Spain. The forest produces mainly pine trees for timber and eucalyptus for paper pulp. Both species are fast-growing and very prone to wildfires.
Issue and measures adopted
The vulnerability of the pine and eucalyptus trees to wildfire has been a problem in an area were wildfires are common during the summer period. In this context, and in order to reduce the wildfire risk and obtain more products from their forests, Vincios locals found inspiration in innovative enterprises and in research groups from the University of Vigo.
Based on the findings made by the enterprises and researchers, several measuresaiming to face wildfire risks and increase benefits have been taken, namely:
- Building a compost plant, to process the excess of biomass from the forests and reduce fire risk.
- Chestnut and oak trees have been planted in the best soils of the forest. These slow-growing species are less prone to wildfires and they produce high quality wood, as well as chestnuts that can be sold in a good price.
- Trekking paths have been created and visitors can find information on the benefits of the forest through a specially developed smartphone application.
- Wild horses are bred to feed on scrubland.
- Pastures have been created to breed sheep.
Which are the benefits obtained so far?
Some of the benefits obtained thanks to the applied measure are:
- The increase of the forest diversification, as well as its water filtering and storage capacity. This has improved the water quality of the neighbouring Zamáns reservoir, which supplies water to the city of Vigo.
- High quality honey is produced.
- Studies from the University of Vigo have shown that these investments in multifunctionality have greatly increased the economic, social and ecological benefits for the area.
Why is forest diversification interesting for mountain areas?
The specific natural conditions of mountain forests (slope, climate, soils) make their exploitation difficult. Equally, the critical ecosystem services provided by forests must be taken into consideration. At the same time, in many countries the size of the forest owned by mountain actors is not too big, being necessary to combine the forest management with other economic activities.
Consequently, Euromontana considers that adapted solutions have to be developed and implemented to ensure that individuals and enterprises working in mountain forests participate in, and benefit from, the sustainable development of the forest related supply chains. This sustainability could be achieved not only, but also through diversification activities as the one showed by this good practice.
For more information, please, visit the Vincios Heritage website.
27 February 2015